Physical fitness not only strengthens the body but also enhances cognitive functions like memory, focus, and problem-solving, while reducing the risk of cognitive decline.
This in-depth article explores the crucial connection between fitness and cognitive health and how incorporating regular physical activity into your life can not only improve your body but also supercharge your mind.
Exercise Boosts Memory and Learning Capacity:

The hippocampus is the part of the brain responsible for memory and learning, and it is especially responsive to the effects of physical activity. Regular exercise, particularly aerobic activities, helps to stimulate neurogenesis, the process of creating new brain cells, especially in the hippocampus. The result? A stronger memory and an enhanced ability to learn new information.
- Scientific Insight: Studies show that exercise increases the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports the growth and maintenance of neurons. BDNF is often referred to as “fertilizer for the brain” because it nurtures the connections between neurons, aiding in learning and memory retention.
- Practical Benefit: Whether you are studying for an exam, learning a new skill at work, or trying to remember names and faces, regular exercise can boost your cognitive ability to learn and recall information. People who engage in regular physical activity often report sharper memory and quicker recall of facts, which can be particularly beneficial as we age.
Improves Focus, Attention, and Concentration:
Distractions are part of modern life—whether it’s digital notifications or just the mental clutter that comes with multitasking. Fitness can be an effective tool to enhance focus and improve concentration.
When you exercise, your body pumps more oxygen to the brain, which supports better brain function. Physical activity also triggers the release of key neurotransmitters, like dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine, which help you stay focused and engaged.
- Scientific Insight: Research published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine shows that exercise enhances the brain’s ability to filter out distractions and stay focused on a task. This is because physical activity stimulates the prefrontal cortex, the area of the brain responsible for decision-making, concentration, and self-regulation.
- Practical Benefit: For those struggling with focus—whether it’s staying attentive in a meeting, completing a project, or concentrating on a creative task—regular physical activity can provide a significant boost. Just 30 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, can improve attention span and mental clarity for several hours after the workout.
Reduces the Risk of Cognitive Decline and Dementia:
As we grow older, the risk of cognitive decline increases. Conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia become more common with age. Fortunately, engaging in regular exercise is one of the most effective ways to lower the risk of these debilitating conditions.
Studies show that physically active individuals are less likely to develop Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia compared to those who lead sedentary lifestyles.
- Scientific Insight: Exercise increases cerebral blood flow, delivering more oxygen and nutrients to the brain, which helps maintain brain health. Moreover, regular physical activity enhances brain plasticity, which is the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize neural pathways. This makes the brain more resilient to damage from aging and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Practical Benefit: For middle-aged and older adults, maintaining a regular fitness routine can significantly reduce the risk of cognitive disorders in later life. Activities like walking, swimming, dancing, or even resistance training are not only beneficial for physical health but also act as protective measures for long-term brain health.
Also Read: Do Local Gyms Teach Yoga Classes – Classes, Benefits, and More!
Reduces Anxiety, Stress, and Depression, Enhancing Cognitive Performance:
Mental health plays a crucial role in cognitive function. Chronic stress, anxiety, and depression can have a detrimental effect on brain health, impairing memory, focus, and overall cognitive function. Regular physical activity is an effective natural remedy to combat these conditions. Exercise releases endorphins—known as the “feel-good” chemicals—which improve mood and alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Scientific Insight: Physical activity reduces levels of cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone. High levels of cortisol can damage the brain over time, particularly areas involved in memory and learning. Exercise also increases levels of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine—neurotransmitters that help regulate mood and mental clarity.
- Practical Benefit: If you’re feeling mentally drained or overwhelmed, engaging in physical activity, even for a short period, can lift your mood, reduce stress, and improve your cognitive abilities. Regular exercise promotes emotional resilience, better sleep, and a clearer mind—all of which are crucial for optimal brain function.
Boosts Creativity and Problem-Solving Skills:
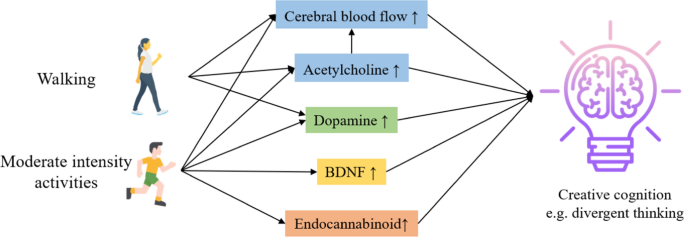
Physical activity doesn’t just improve structured cognitive tasks like memory and attention; it also boosts creativity and problem-solving. Many people find that their best ideas or solutions to difficult problems come to them during or after a workout. This is no coincidence—exercise promotes cognitive flexibility, enabling the brain to shift between thoughts and find new solutions.
- Scientific Insight: A study published in the Journal of Experimental Psychology found that individuals who engage in regular physical activity are more likely to experience moments of creative insight. The increased blood flow to the brain, particularly to the prefrontal cortex, improves divergent thinking (the ability to generate multiple solutions to a problem), which is crucial for creative problem-solving.
- Practical Benefit: If you’re facing a mental block or need to come up with creative ideas, incorporating a workout or even a simple walk into your day can stimulate creative thinking. Physical activity helps clear mental fog, allowing for a more innovative and flexible mindset.
Supports Brain Plasticity and Cognitive Flexibility:
Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is the brain’s capacity to reshape and reorganize itself by creating new neural connections. This is crucial for learning new things, recovering from injuries, and adapting to changes. Fitness plays a significant role in enhancing brain plasticity by stimulating the growth of new neurons and synapses.
- Scientific Insight: Exercise boosts levels of BDNF, a protein that promotes the growth of new neurons and strengthens existing ones. This enhances the brain’s ability to rewire itself and adapt to new learning experiences or recover from trauma, such as a stroke.
- Practical Benefit: By staying physically active, you are continuously stimulating your brain’s capacity for growth and adaptation. This can help you learn new skills more easily, solve complex problems, and bounce back from setbacks faster—both mentally and emotionally.
Strengthens Executive Function for Better Decision-Making:
Executive function is a set of cognitive processes that includes working memory, flexible thinking, and self-control. These are critical for planning, decision-making, and managing time effectively. Physical exercise, particularly activities that challenge coordination and focus like yoga, martial arts, or team sports, can significantly strengthen executive function.
- Scientific Insight: Studies have shown that exercise, particularly aerobic exercise, enhances connectivity between different regions of the brain, improving executive function. This includes better decision-making, impulse control, and the ability to set and achieve goals.
- Practical Benefit: If you find it difficult to stay organized or make quick decisions, regular exercise can help enhance your executive functioning skills. Activities that require both physical and mental engagement, such as yoga, tennis, or even hiking, are especially effective at sharpening these cognitive processes.
Also Read: What Oil Filter For Kohler Fits 725 Series Kohler Engine – A Complete Guide!
Fitness and the Impact on Neurotransmitters:
Physical activity doesn’t just benefit the structure of the brain—it also plays a significant role in balancing neurotransmitters, the chemicals that facilitate communication between neurons. The regulation of neurotransmitters like dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine is essential for cognitive functions such as mood, motivation, and attention.
- Scientific Insight: When you exercise, the brain releases dopamine, which is involved in motivation and reward-based learning. It also boosts serotonin levels, which helps regulate mood and sleep—both of which are critical for optimal brain function.
- Practical Benefit: Regular exercise can help maintain balanced neurotransmitter levels, preventing mental fatigue and enhancing mood. This balance is crucial for staying motivated, focused, and emotionally stable, all of which contribute to better cognitive performance.
FAQ’s
1. How does exercise improve memory?
Exercise stimulates neurogenesis in the hippocampus, which boosts memory and learning by encouraging the growth of new brain cells.
2. Can fitness help with focus and concentration?
Yes, physical activity increases oxygen flow to the brain and releases neurotransmitters that improve attention, focus, and concentration.
3. Does regular exercise reduce the risk of cognitive decline?
Yes, studies show that regular physical activity lowers the risk of cognitive decline, dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease, especially in older adults.
4. How does exercise help with mental health issues like stress or anxiety?
Exercise releases endorphins and reduces cortisol, helping alleviate stress, anxiety, and depression, which in turn enhances cognitive function.
5. Does fitness improve creativity and problem-solving?
Physical activity promotes cognitive flexibility, allowing the brain to generate new ideas and solve problems more effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fitness plays a pivotal role in enhancing cognitive health by boosting memory, focus, and problem-solving abilities while reducing the risk of cognitive decline and mental health issues. Regular exercise stimulates neurogenesis, improves brain plasticity, and balances neurotransmitters, making it essential for maintaining mental sharpness and emotional resilience. Incorporating physical activity into your daily routine not only strengthens the body but also supercharges the mind for long-term cognitive well-being.